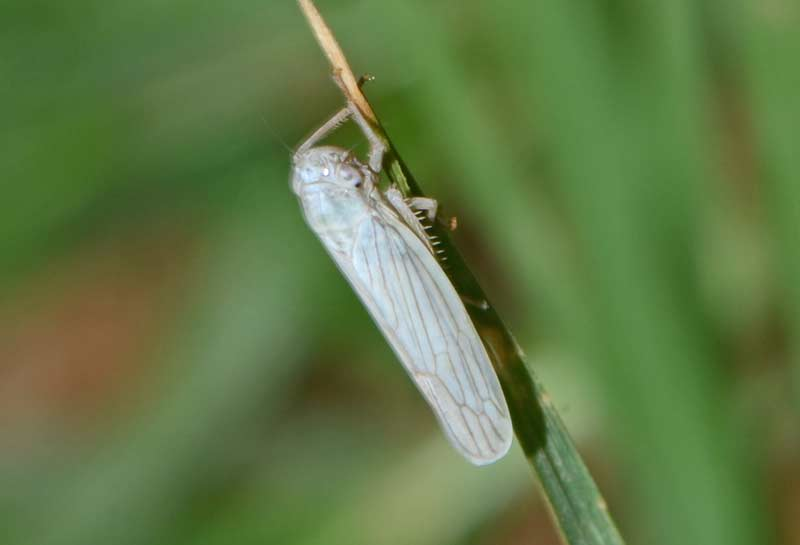
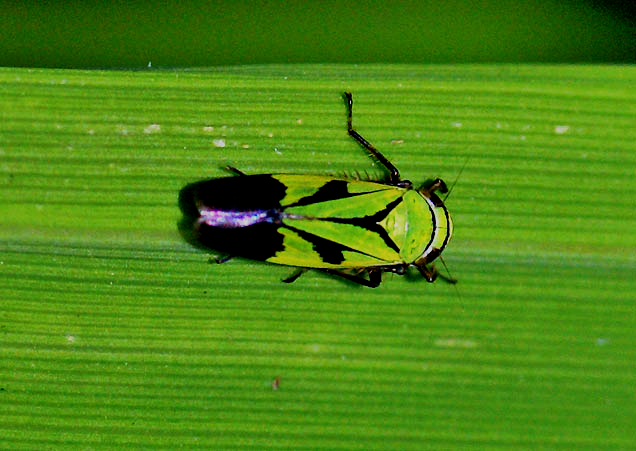
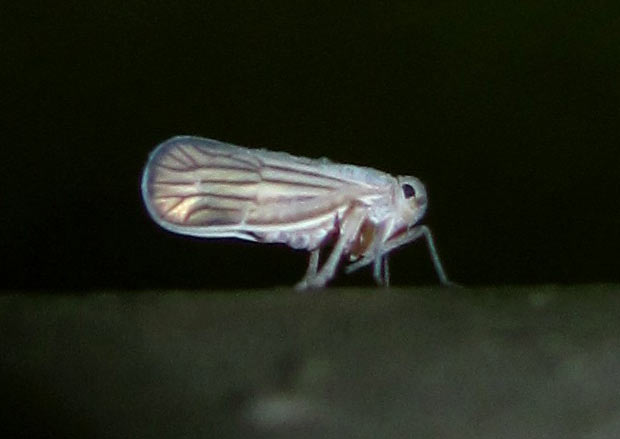
Symptoms
- Leaf hoppers suck up the plant sap causing withering of the plants
- In cases of severe attack the growth get stunted and the plants wither away ultimately.
- Green leaf hoppers transmit tungro, virus and transitory yellowing virus diseases.
Procedure for Observation
Randomly mark 4 one sq.meter plots per 0.4 Ha. Select five hills at random per m.sq. and take quick count of adult and nymphs without disturbing the plants.